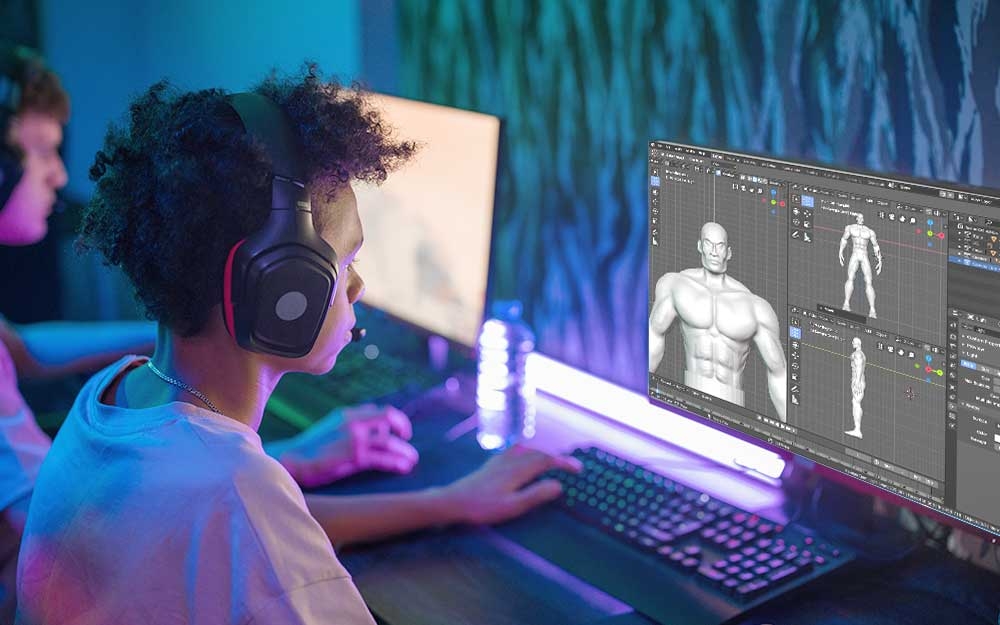
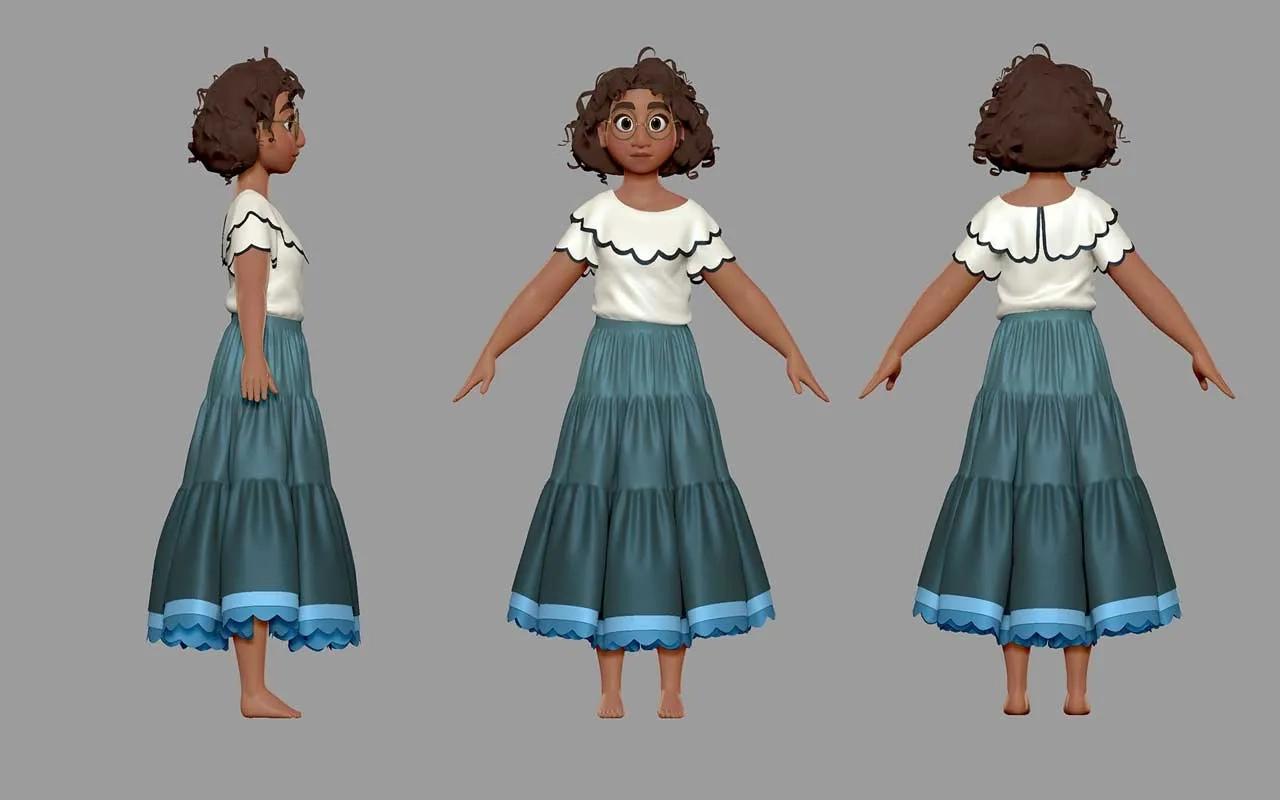
What is 3D Modeling?
3D modeling is the process of creating a three-dimensional representation of a physical object or scene using specialized computer software. This model can be manipulated, visualized, and modified in a digital environment before it is either printed (in 3D printing) or used in animation, games, simulations, etc.
Types of 3D Modeling
There are several types of 3D modeling techniques, each suited for different purposes. Some of the most common types include:
-
Polygonal Modeling:
-
Description: This is the most common type of modeling used for games and films. It involves creating a 3D object by defining its surface with polygons, typically triangles or quadrilaterals. The model is made up of many small, flat faces (polygons) that form the overall shape.
-
Applications: Used for game characters, environments, and animation.
-
-
NURBS Modeling (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines):
-
Description: NURBS modeling uses curves to create smooth, flowing surfaces. This type of modeling is ideal for creating highly detailed, organic shapes like cars, aircraft, or human figures.
-
Applications: Industrial design, automotive design, and character modeling for animation.
-
-
Spline Modeling:
-
Description: Spline modeling uses curves and lines to define the shape of a 3D object. These curves are then converted into a 3D surface.
-
Applications: Often used in architecture, automotive, and character modeling.
-
-
Voxel Modeling:
-
Description: In voxel modeling, objects are represented by tiny cubes (voxels) rather than polygons. It’s similar to pixel-based art, but in three dimensions.
-
Applications: Video games (like Minecraft), scientific visualization, and medical imaging.
-
-
Procedural Modeling:
-
Description: This method uses algorithms and mathematical functions to automatically generate 3D models. It’s commonly used for creating large-scale environments or complex textures.
-
Applications: Game environments, landscapes, and procedural animations.
-
-
3D Scanning:
-
Description: 3D scanning is the process of using a scanner to capture the physical properties of an object or environment and convert it into a digital 3D model.
-
Applications: 3D printing, cultural heritage preservation, industrial inspection, and virtual reality.
-
Key 3D Modeling Software
Several software tools are commonly used for creating 3D models. The choice of software often depends on the type of modeling required and the specific application:
-
Blender:
-
Overview: Blender is a popular, open-source 3D modeling software. It supports modeling, texturing, rendering, and animation, and is used for creating both 3D models and animated scenes.
-
Strengths: Free, highly flexible, great community support, and extensive tutorials.
-
Applications: Animation, game design, VFX, and product visualization.
-
-
Autodesk Maya:
-
Overview: Maya is a powerful 3D modeling and animation software used by professionals in film, television, and game development.
-
Strengths: High-end modeling and animation tools, excellent for character rigging and animation.
-
Applications: Film production, animation, video game development.
-
-
Autodesk 3ds Max:
-
Overview: 3ds Max is used primarily for architectural visualization, game development, and product design. It has powerful modeling and rendering features.
-
Strengths: User-friendly interface, powerful rendering capabilities, and strong for architectural models.
-
Applications: Game development, architectural visualization, and product design.
-
-
Cinema 4D:
-
Overview: Cinema 4D is a 3D modeling, animation, and rendering software known for its easy-to-use interface and powerful motion graphics capabilities.
-
Strengths: Great for motion graphics, visual effects, and quick learning curve.
-
Applications: Motion graphics, animation, and product visualization.
-
-
ZBrush:
-
Overview: ZBrush is a specialized software for sculpting high-resolution 3D models. It’s often used for creating detailed organic shapes like characters, creatures, and facial features.
-
Strengths: Exceptional sculpting tools, great for organic modeling, used in film and game character design.
-
Applications: Character modeling, digital sculpture, and game development.
-
-
SketchUp:
-
Overview: SketchUp is a user-friendly 3D modeling software used primarily for architectural design, interior design, and urban planning.
-
Strengths: Easy to learn, excellent for architecture, and has a large library of pre-made models.
-
Applications: Architecture, interior design, urban planning, and product design.
-
-
Fusion 360:
-
Overview: Fusion 360 is a cloud-based 3D modeling tool for product design and engineering, often used in industrial design and manufacturing.
-
Strengths: Collaborative design, CAD tools, parametric modeling, and cloud integration.
-
Applications: Product design, engineering, and manufacturing.
-
-
Tinkercad:
-
Overview: Tinkercad is an easy-to-use online 3D design tool, perfect for beginners and hobbyists. It allows users to create simple 3D models, which can be exported for 3D printing.
-
Strengths: Free, simple to use, browser-based, and good for learning 3D modeling.
-
Applications: 3D printing, educational projects, and quick prototyping.
-
How to Get Started with 3D Modeling
-
Learn the Basics: Start with free or beginner-friendly software like Blender or Tinkercad to get a feel for 3D modeling.
-
Tutorials: Many platforms offer free tutorials on YouTube, Udemy, and other educational websites. Websites like CG Cookie, Blender Guru, or Pluralsight offer in-depth learning resources.
-
Practice: The best way to improve your skills is through consistent practice. Start small, and work on building simple models like everyday objects.
-
Join Communities: Engage with online communities, such as forums and social media groups, where 3D artists share tips and feedback.